Battle of Hastings Quiz
Test your knowledge of the Battle of Hastings with our 20 Questions Quiz.
-
Q1. Which king of England died on 5 January 1066, leaving no direct heirs?
Answer: Edward the Confessor
King Edward the Confessor died on 5 January with no direct heirs. Earl Harold of Wessex, the Confessor’s brother-in-law and a powerful noble, was proclaimed king and crowned at Westminster Abbey the next day. But there were two other rival claimants to the throne: Harald Hadrada, King of Norway, and William, Duke of Normandy. Both prepared to invade to capture the English throne.
-
Q2. Whom did Harold defeat in a battle at Stamford Bridge, just before the Battle of Hastings?
Answer: Harald Hardrada
On 25 September, Harold defeated Harald Hadrada, King of Norway and claimant to the English throne, in a hard-fought battle at Stamford Bridge, near York.
-
Q3. Where did the Normans land in England?
Answer: Pevensey Bay
William's fleets assembled off the River Dives, north-east of Caen, on about 12 August, but were prevented from sailing by unfavourable winds. After a storm drove the fleets east to the port of St Valéry, a desperate William sought the assistance of St Valéry himself, and eventually crossed the Channel on the night of 27 September.
-
Q4. Roughly how large were each of the two armies at the Battle of Hastings, 1,000-2,000 men, 5,000-7,000 men or 10,000-12,000 men?
Answer: 5,000–7,000 men
There has been much debate regarding the size of the two armies but the latest thinking is that both armies had between 5,000 and 7,000 men – large forces by the standards of the day.
-
Q5. What was notable about William’s minstrel, Ivo Taillefer?
Answer: He struck the first blow in the Battle of Hastings
William's minstrel, Ivo Taillefer (whose name means 'hewer of iron') killed the first Saxon of the battle. The Carmen de Hastingae Proelio (Song of the Battle of Hastings) says that a Saxon soldier broke ranks and was killed by Taillefer. But other sources say that Taillefer charged into the enemy shield wall, where he killed several Saxons before he was overwhelmed.
-
Q6. What were the ‘housecarls’?
Answer: The military and social elite of Anglo-Saxon England.
Highly trained soldiers, many were nobles and provided Harold’s bodyguard. These fearsome Anglo-Saxon warriors were among the finest soldiers in Europe. Their favourite weapon was a long-handled battleaxe, which was capable of cutting off the head of a man or horse.
-
Q7. Why did some of William’s forces on the left flank flee in panic?
Answer: They heard a rumour that the duke had been killed
To stop panic spreading and rally his troops, William rode out in front of them, raised his helmet to show his face and shouted, 'Look at me! I live and, with God's help, I shall conquer!'
-
Q8. For how long did the Battle of Hastings last?
Answer: Over nine hours
The battle lasted from dusk till dawn – an exceptionally long time for a medieval battle. It ended when William of Normandy defeated King Harold of England. The battlefield is actually eight miles from Hastings.
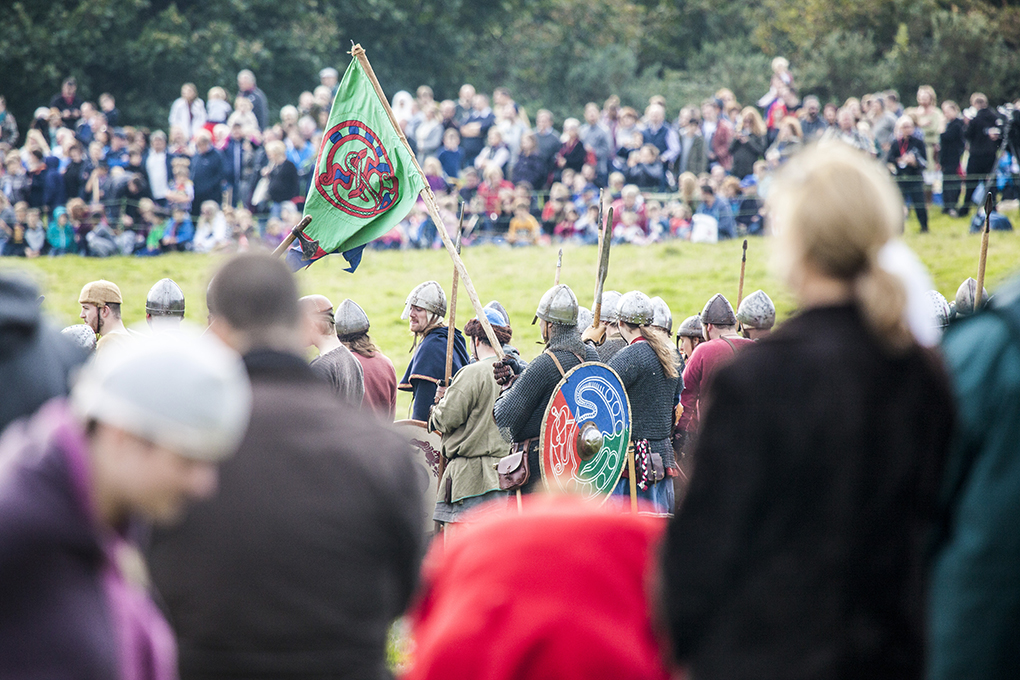

-
Q9. William’s forces killed large numbers of Englishmen by twice using what tactic?
Answer: Feigning retreat
William's foot soldiers and cavalry drew English soldiers from their positions by twice feigning retreat before turning around and counter-attacking. The result was that Harold's army was split, giving up the high ground and breaking its shield wall. (Inconsistencies in the sources mean that we can’t be sure that William’s army feigned retreat twice. The Carmen de Hastingae Proelio, for instance, describes William’s army as feigning retreat and then genuinely retreating.)
-
Q10. What animal played a decisive role in the Battle of Hastings?
Answer: The horse
The English army fought on foot at the Battle of Hastings, and ultimately could not withstand the charges of the mounted Norman knights. Although the horses ridden by the Normans were small by modern standards (no bigger than ponies), the knights had substantial wooden saddles and well-designed stirrups, giving their lances impressive striking force.
-
Q11. The Bayeux Tapestry appears to show Harold being struck in the eye by an arrow. But how does an earlier source say Harold died?
Answer: He was hacked to death by four Norman knights
The account reads: 'The first, cleaving his breast through the shield with his point, drenched the earth with a gushing torrent of blood; the second smote off his head below the protection of the helmet and the third pierced the inwards of his belly with his lance; the fourth hewed off his thigh and bore away the severed limb.'
-
Q12. Which abbey housed the supposed grave of King Harold?
Answer: Waltham Abbey
Early sources say that William denied Harold's mother his body, which was buried on unconsecrated ground near the shore. However, later sources report that Harold's mutilated body was identified by his mistress and buried at Waltham Abbey in Essex, a monastery to which Harold showed special favour. A stone now marks the location of the alleged grave, which would have been inside the abbey church, but has been in the open air since half of the church was demolished after the abbey was Suppressed in 1540 by Henry VIII.
-
Q13. For whom was the Bayeux Tapestry supposedly made?
Answer: Bishop Odo of Bayeux
The tapestry tells the story of events from 1064 until the end of the Battle of Hastings, and was probably made soon after the conquest. It’s been plausibly suggested that it was made for William's half-brother, Bishop Odo. He’s depicted prominently on the Tapestry.
-
Q14. When was William crowned the new king of England?
Answer: 25 December 1066
William was crowned king at Westminster Abbey on Christmas Day 1066 but not everything went to plan. When the congregation shouted their assent to William's rule, the Normans on guard outside the church mistook the noise for treachery and began setting fire to the surrounding buildings. Those inside the buildings ran out to protect their property or join in the looting.
-
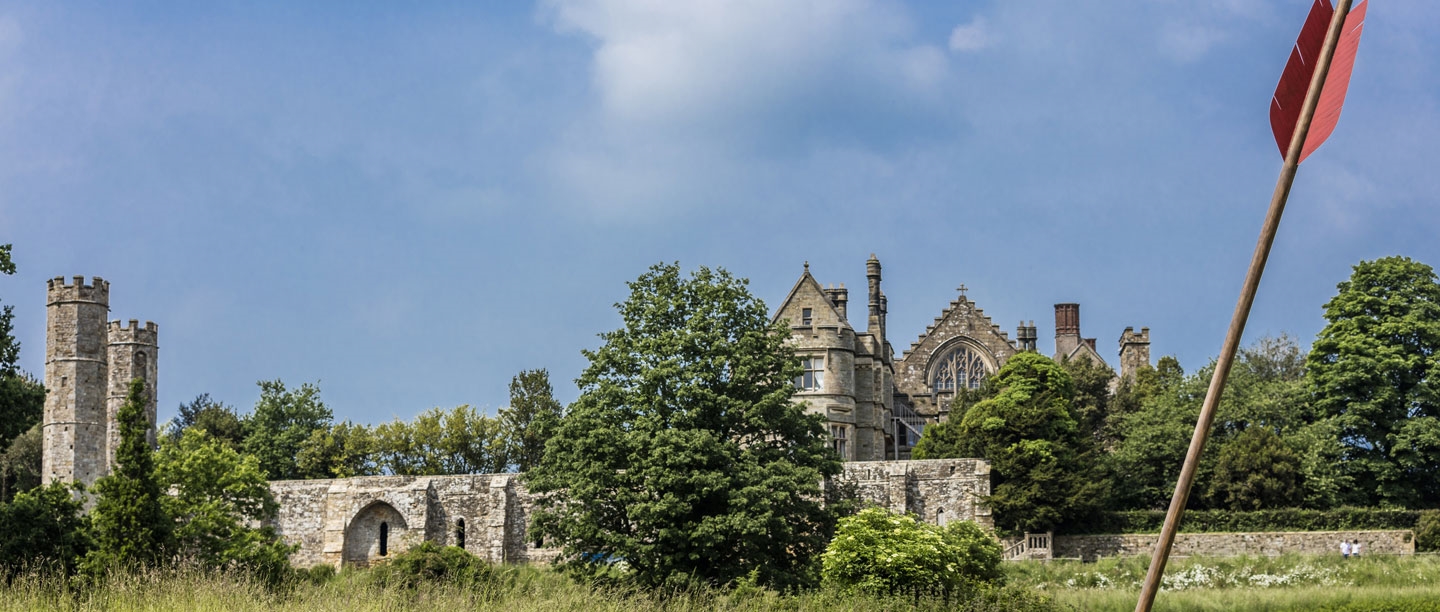
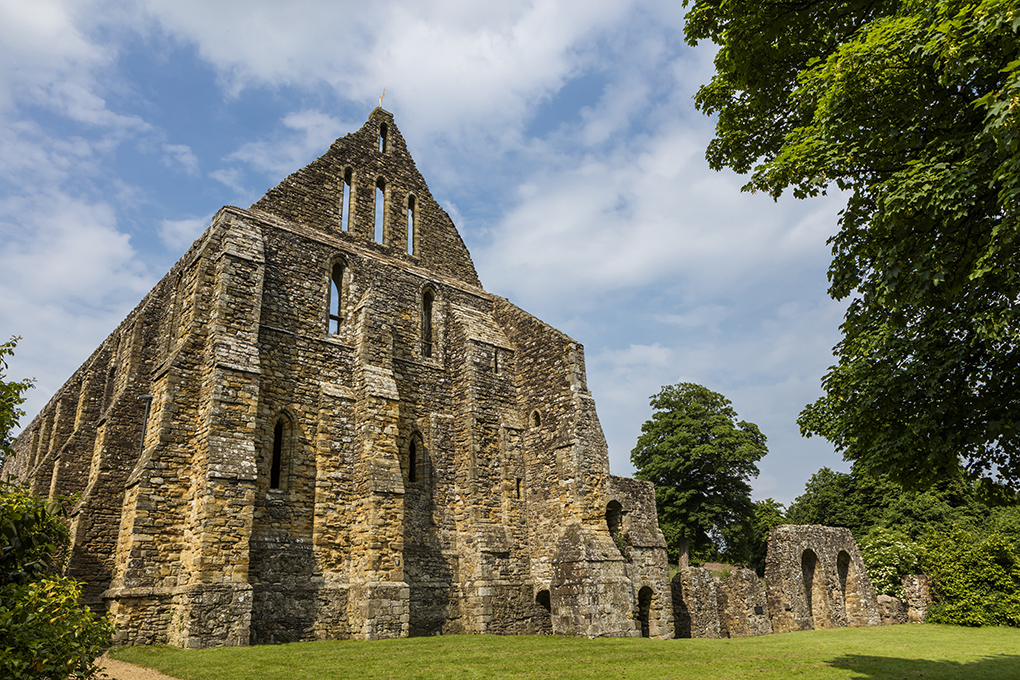
Q15. Why did William build the Benedictine abbey at Battle?
Answer: To atone for the bloodshed of the battle
Even by the standards of the Middle Ages, the Norman Conquest was exceptionally bloody and brutal. William and his supporters feared they might go to hell as a consequence, William founding Battle Abbey as a penance and as a symbol of his great victory. The abbey was founded on the top of the hill where the battle was fought. Its high altar marks the place where Harold was killed – there is now a stone marker on the spot.

-
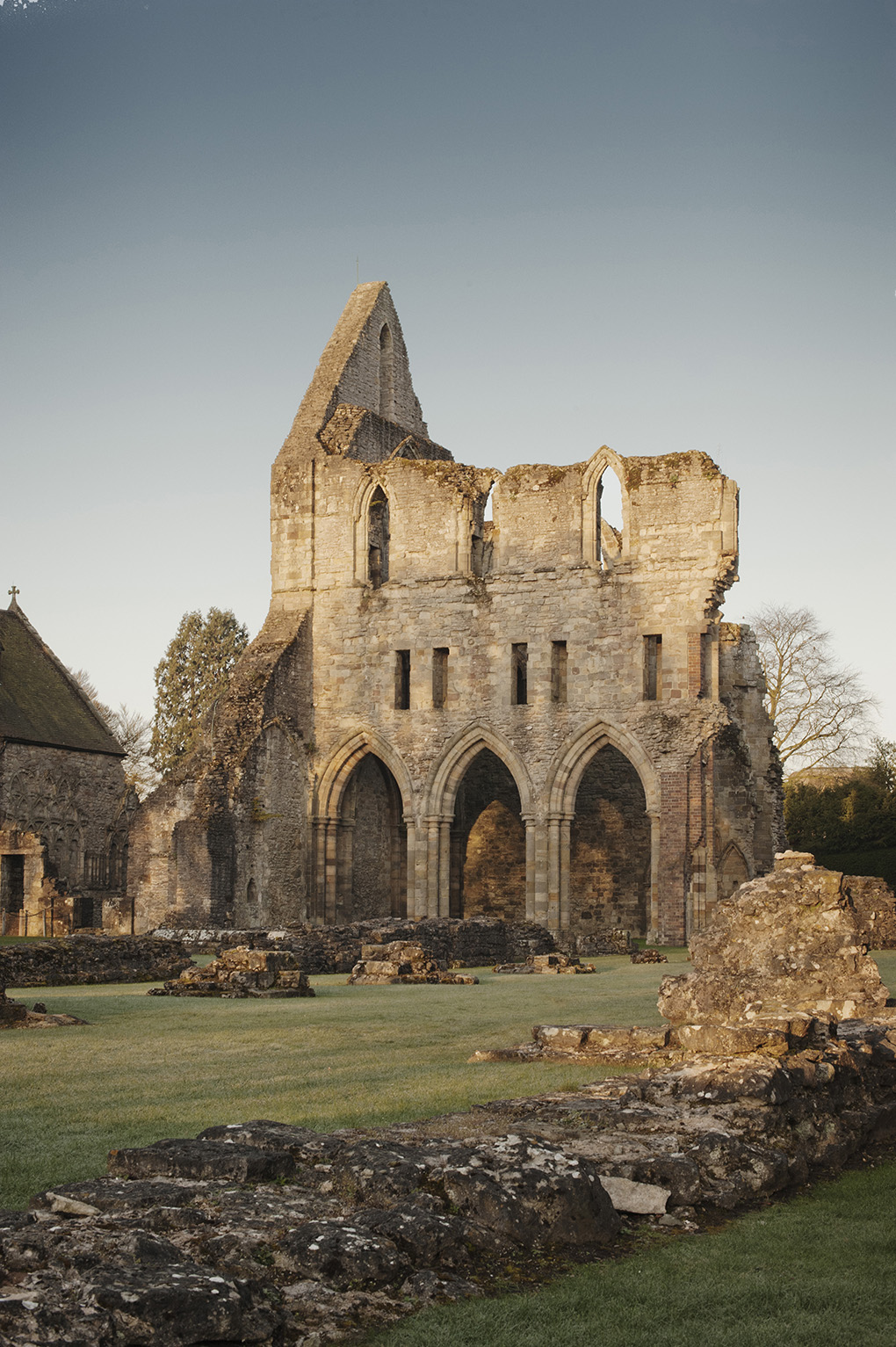
Q16. Answer
Answer: Wenlock Priory
Wenlock Priory in Shropshire was founded in about 1080 by by Roger of Montgomery, Earl of Shrewsbury, as a priory of Cluniac monks. He also established a Benedictine monastery in Shrewsbury.
-
Q17. William was king of England until his death in 1087. Who succeeded him?
Answer: William II
William II was William the Conqueror's son and was king of England until 1100. He made generous gifts to Battle Abbey but earned a reputation as a brutal and corrupt tyrant. He was shot in the back with an arrow and killed while hunting in the New Forest.
-
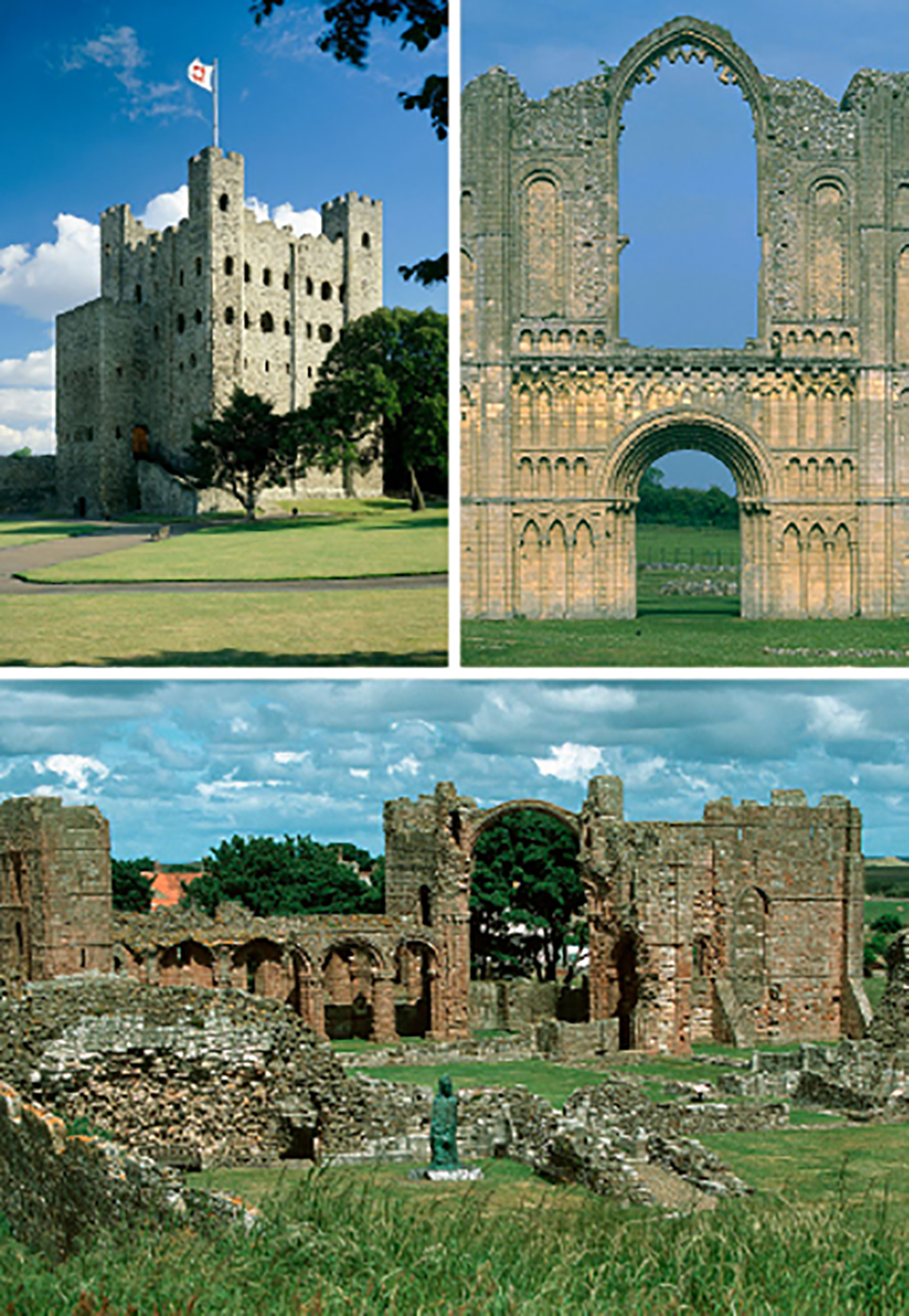
Q18. Answer
A. Rochester Castle (keep)
B. Castle Acre Priory (west front)
C. Lindisfarne Priory
-
Q19. Why did the number of monks at Battle Abbey drop from 52 to 34 in 1348–49?
Answer: They were killed by the Black Death
The Black Death killed between a third and a half of England's population. It is believed to have been the result of a plague, which was probably transmitted from rodents to humans by the bite of infected fleas.
-
Q 20. Who did Henry VIII give Battle Abbey to in 1538?
Answer: Sir Anthony Browne
Following the Suppression of the Monasteries, Henry VIII gave Battle Abbey to his friend Sir Anthony Browne, who demolished much of the monastery, turning the abbot’s house into a mansion. Ironically, his descendants were staunch Catholics and their house at Battle was dubbed ‘little Rome.’